Early childhood development
Together, let’s ensure young children get the assistive technology they need.
©ALTSO
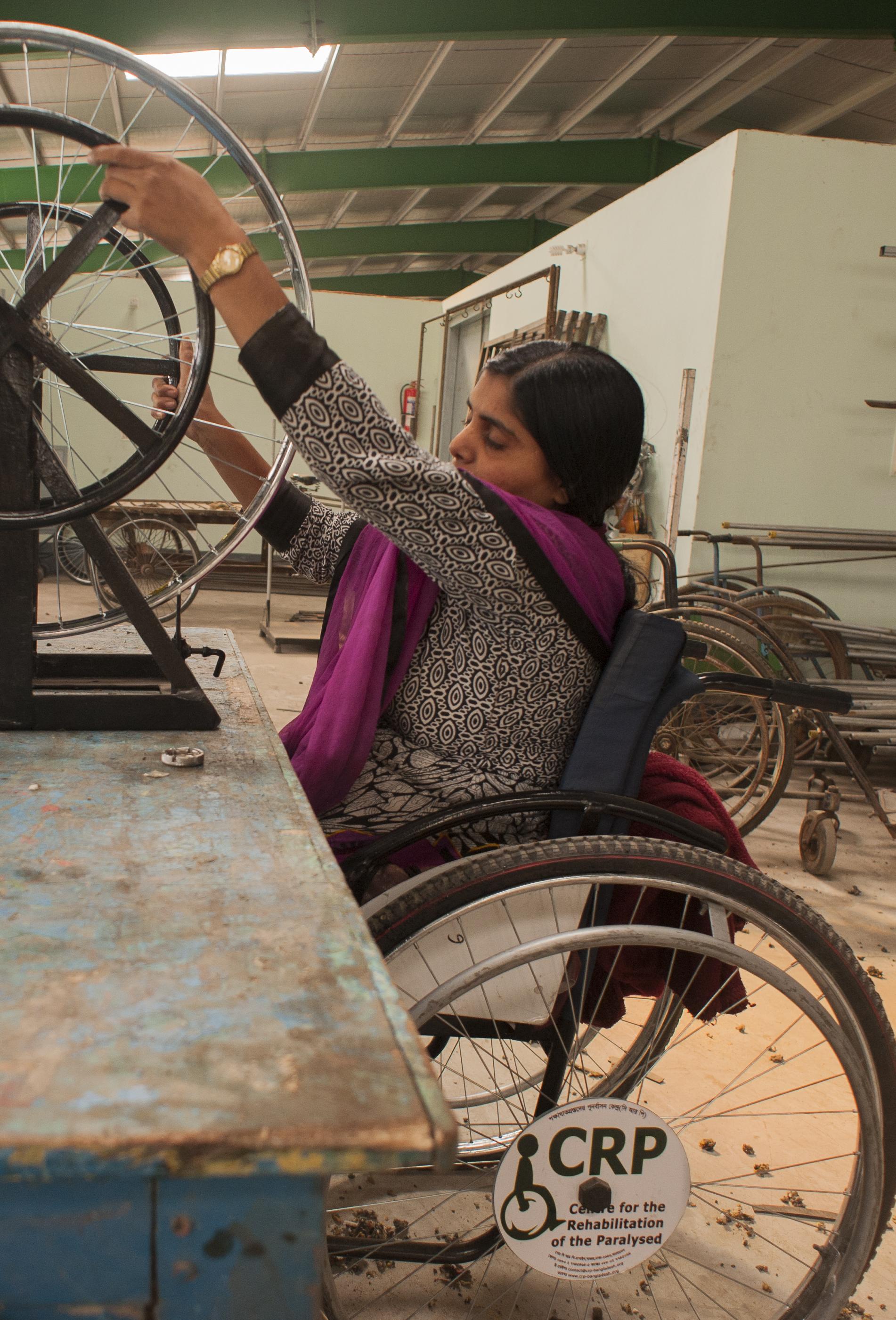
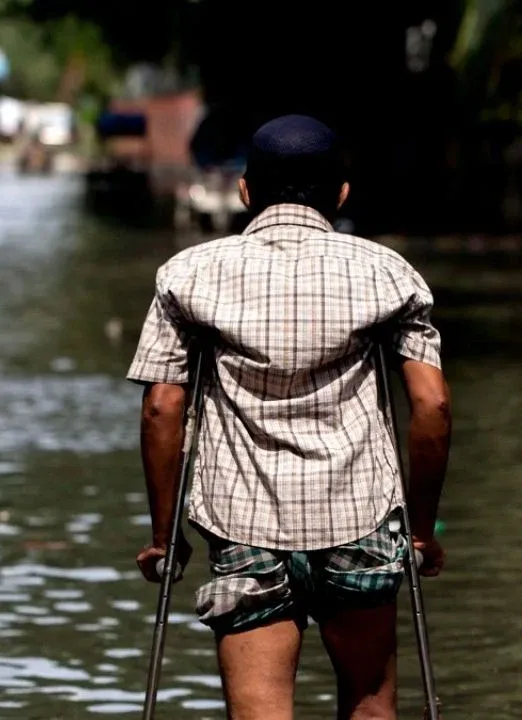
Investing in assistive technology is important for people’s lives from early childhood to old age, and across multiple sectors. The relevance of assistive technology to people’s lives is too big to ignore.
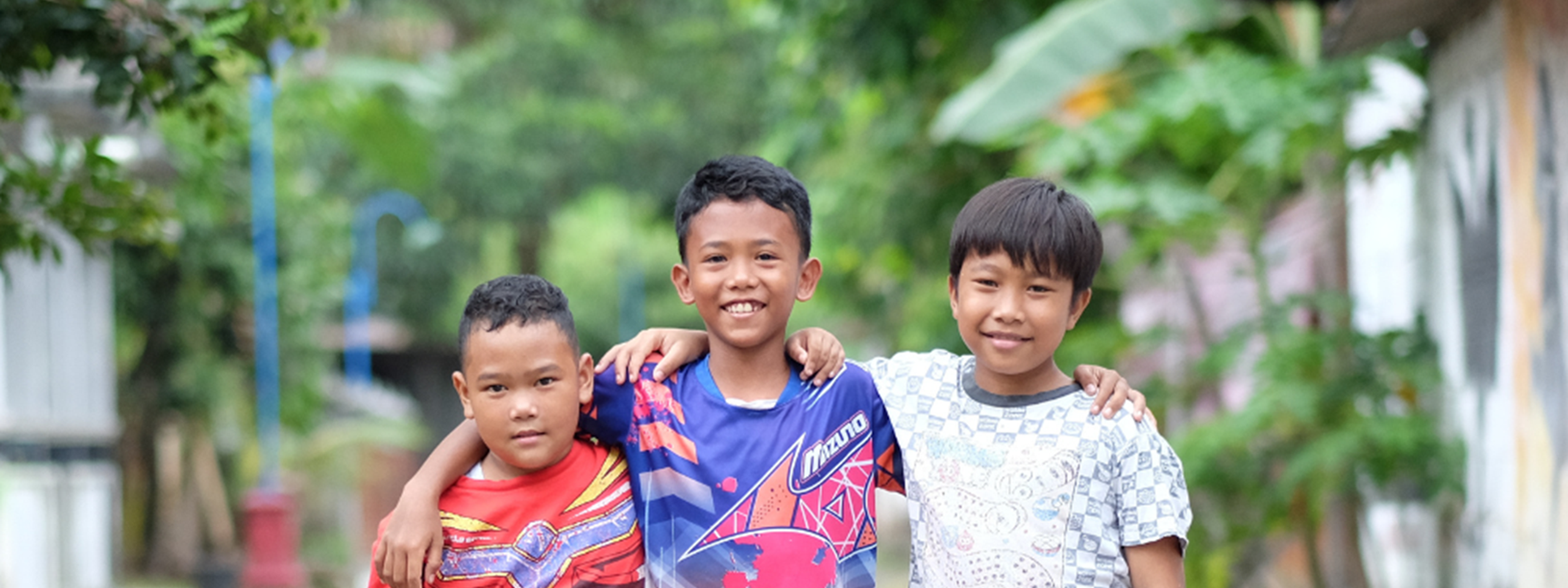
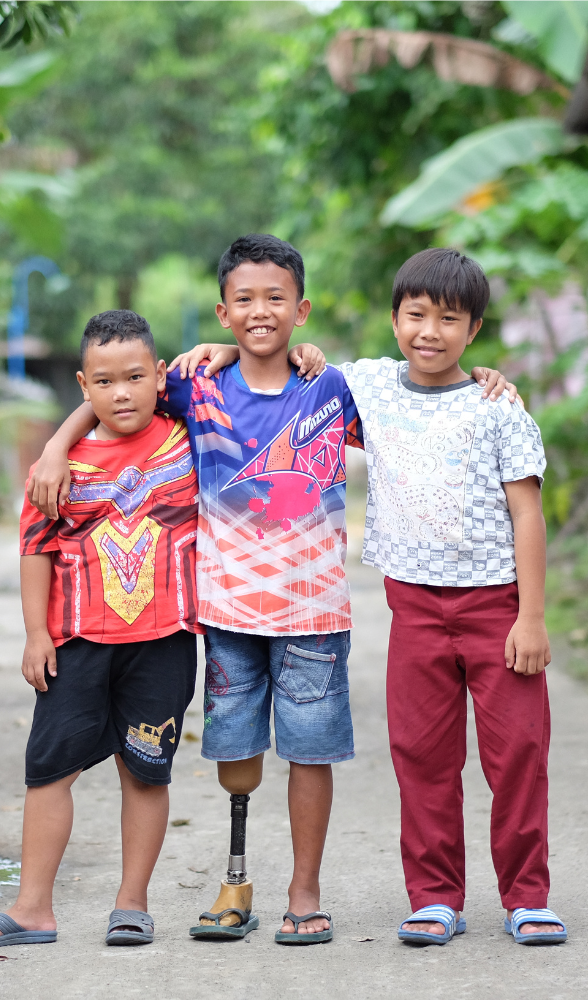
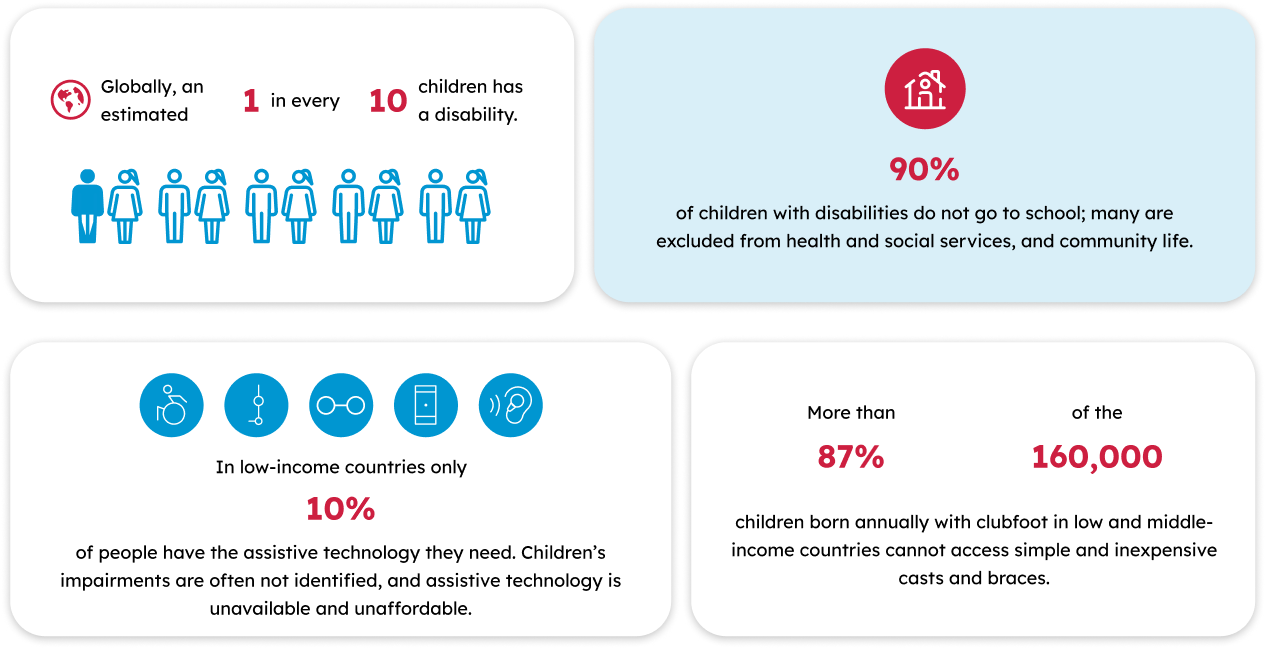
For young children, having access to assistive technology such as glasses, hearing aids, wheelchairs, or digital devices for communication is transformational for lifelong outcomes. Early childhood (age 0-8) is a crucial time of life when cognitive, physical, language, motor skills, social and emotional development occurs. In low-income countries, children with disabilities - and girls more so than boys - face major challenges affecting their early development, and young children without access to assistive technology may be excluded from critical early childhood development (ECD) interventions
Why assistive technology matters for early childhood development
| Early assessment and assistive technology support are crucial for lifelong development. |
| |
| Young children without assistive technology may be excluded from early childhood development opportunities. | ||
| Assistive technology interventions create long-term economic benefits for individuals, carers, and families. |
Inclusion is key to realize the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and leave no one behind. There will not be full inclusion while people are unable to access assistive technology. Assistive technology cuts across all 17 SDGs and is particularly relevant to some.